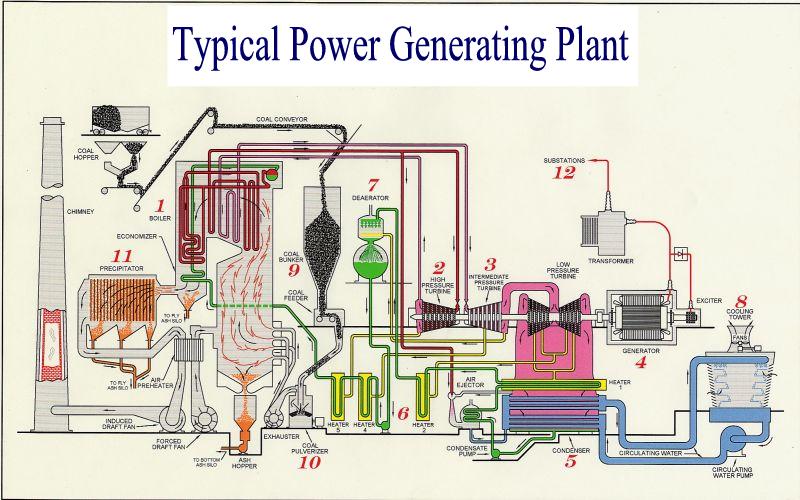
 |
Explore how electric power is generated. Click on the numbers in the image below to discover different function at the typical power plant.
 |
No. 1 - The Boiler
This typical boiler is constructed of approximately 300
miles of special high temperature steel tubing supported by a steel I-beam
frame. The steel tubes are filled with water. Heat inside the
boiler boils the water, and they steam is collected at the top of the boiler.
The steam then flows to the turbine. Ash is collected at the bottom of the
boiler and precipitator, where it is conveyed to an ash collection system.
Coal handling system
This Generating Station burns coal delivered by train.
Coal is delivered to the plant in rail cars that hold 100 tons each. Once
the coal is delivered to the plant, it is unloaded by coal handlers and either
stored in a stock pile for future use or is transferred via coal conveyors into
the plant for immediate use.
No. 2 - High
pressure turbine
The high pressure turbine primarily consists of fan-type blades attached to a
shaft. Steam flows against the blades, causing the shaft to turn.
No. 3 -
Intermediate and low pressure turbine
The intermediate and low pressure turbine, while constructed like the high
pressure turbines, are designed to add efficiency to the cycle.
No. 4 - The generator
The shaft of the generator is connected to the turbine shaft. When the
turbine rotates the generator, electricity is produced.
No. 5 - Condenser
Steam leaves the turbine, and is admitted to the condenser, where it is cooled
by circulating water. The steam is condensed, and water is pumped back to
then boiler.
No. 6 - Heaters
The heaters are used to heat the water on its return back to the boiler.
Small amounts of steam are removed from the turbine at different pressures to
heat the water.
No. 7 - Deaerator
One of the heaters is called the Deaerator because, in addition to heating the
water, it removes air and other dissolved gases from the water.
No. 8 - Cooling tower
The cooling tower is used to cool the circulating water. This is done by
lowing air across water that is falling through the cooling tower.
Circulating water
pumps
These pumps are used to transfer water from the cooling tower to the
condenser and back to the cooling tower.
No. 9 - Coal bunker
Coal is delivered to the Generating Station by rail. Belt conveyors
are used to transfer the coal to the storage bunkers.
Coal feeders
The coal feeders measure the amount of coal that is required to make steam and
generate power as required by our customers. Coal flow to the boiler
varies as the amount of electricity used varies.
No. 10 - Coal
pulverizer
The coal flows by gravity into the pulverizers from the coal feeders.
When the coal is in the pulverizer, it is ground into the approximately fineness
of talcum powder. It is then blown into the furnace, where it mixes with
air, and burns at bout 2500 degrees Fahrenheit.
Fans
The boiler has two large fans. The forced draft fan blows air into the
boiler so that coal will burn and produce heat to produce steam and the induced
fan pulls gases from the boiler and precipitator.
No. 11 - Precipitator
The electrostatic precipitator eliminates 99.6% of the fly ash from the boiler
flue gases by means of many fine wires and static electricity, so that smoke
from the chimney will be eliminated.
Chimney
The chimney is the final destination of the coal combustion process. It is
typically over 400 feet tall. Boiler controls and plant operators carefully control the
fuel combustion process to keep emissions to a minimum and to ensure that the
maximum amount of heats is extracted from the coal as possible.
Transformer
Electricity from the generator (13,400 volts) travels to the main step up
transformer. It is then converted to 115,000 volts.
No. 12 - Substations
Electricity that is generated will be sent to various satellite substations
located strategically in the electric distribution system. From there, the
circuits are used to transmit electricity to all of our customers:
industrial, commercial, irrigation, rural and residential.